Power Supply Test
Test reports
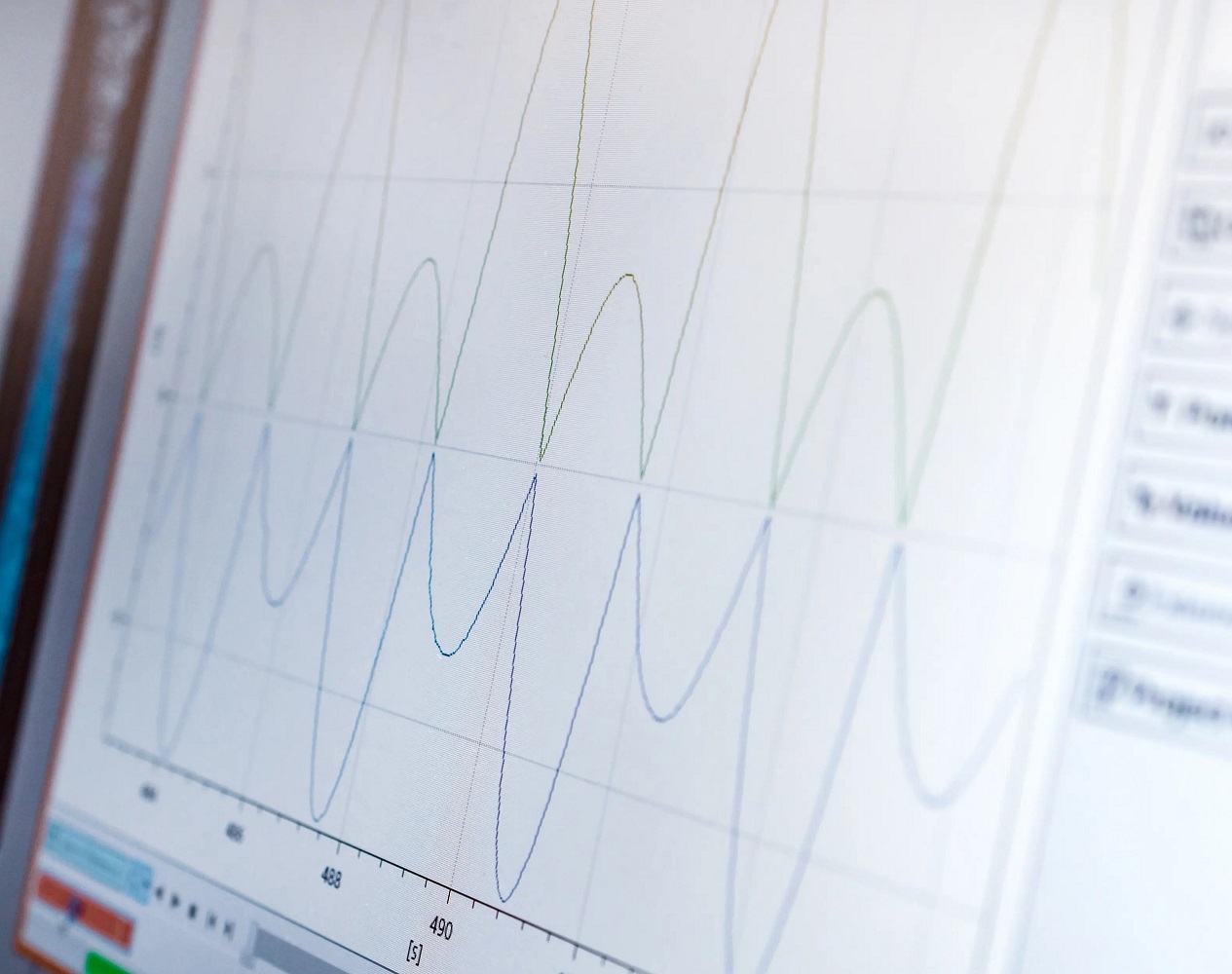
eVision Systems tests the power supply capability of USB ports, chargers and USB power banks and determines the exact power consumption of a USB device. Our tests are subject to strict framework conditions and are implemented with professional tools. You will receive a comprehensive test report for each tested device. An example of a test report result can be found in the link below.
Register demand
Register your test needs to receive a quote with pricing information and information on processing time. If you have any questions about the test procedure or need more information about our USB power supply test, you can use the form included in the link. Please provide the number of devices to be tested, your contact details and any other information needed.
Which USB Ports & Power Supplies Ports & Connectors can be tested?
- DCP (2,5W)
- SDP (2,5W)
- CDP (4,5W)
- USB A (18W)
- USB B (18W)
- Quick Charge (100W)
- Proprietary
Which USB power supply standard can be tested?
| Specification | Voltage | Current | Power |
| USB 1.0 / 1.1 | 5 V | 0.1 A | 0,5 W |
| USB 2.0 | 5 V | 0.5 A | 2,5 W |
| USB 3.0/3.1 | 5 V | 0.9-1.5 A | 7,5 W |
| USB BC 1.2 | 5 V | 1.5 A | 7,5 W |
| USB Type C | 5 V | 3 A | 15 W |
| Quick Charge 1.0 | 6,3 V | 1.5 A | 9,45 W |
| Quick Charge 2.0 | 5V / 9V / 12V | 1.67 A / 2A | 18 W |
| Quick Charge 3.0 | 3.6 V - 22 V (0.2 V Schritte) | 2.6 A / 4.6 A | 36 W |
| Quick Charge 4 | 3,6 V - 22 V (0.2 V Schritte) | 3A | 60 W |
| Quick Charge 4+ | 3,6 V - 20 V (20 mV Schritte) | 3 A / 5A | 100 W |
| USB PD | 5 V / 12 V / 20 V | 5 A | 100 W |
| USB PD with PPS | 3.3 V - 21 V (20 mV Schritte) | 0 A - 5 A (50 mA Schritte) | 100 W |
What is tested?
We check the power supply capability of USB ports, chargers and USB power banks.
To do this, we carry out the following tests
- Verification that a USB host is capable of delivering the specified maximum performance without errors.
- Determination of available USB performance profiles.
- Ensuring voltage levels stay within specification under heavy loads.
- Measurement of electrical residual ripple at 1 KHz.
- Determining the real capacity in mAh (power banks)
- Measurement of communication speed & data integrity of the USB port
- Measurement of the exact power consumption of a USB device.