Universal Serial Bus in the automotive Area
What is the Universal Serial Bus (USB)?
There are hardly any devices that can do without a USB interface. It supports cameras, memory sticks, mice, printers, MP3 players, smartphones and much more for data transfer and power supply. Well-known manufacturers from the computer industry, such as Intel, introduced this standard as early as 1996. Since then, it has been gaining acceptance worldwide and is being further adapted to modern interface requirements, for example with regard to transmission rates. There are now versions 3.0 and 3.1.
How does USB work?
The Universal Serial Bus is based on a serial architecture. This means that the data is transferred bit by bit, in series, from one device to the other. This enables data transfer at high speed and with a low error rate. In addition, there is no need for an additional power cable, as the interface is also used for energy transmission. Data is also sent and received in both directions (I / O interface).
Since 2001 it has been possible to transfer data between two peripheral devices, such as a camera and printer. This technology is called USB On The Go (OTG) and is marked in the USB symbol by a green arrow with the words "On-The-Go". As a rule, the functional options are limited with this type of data transfer. Before this technology was introduced, USB had a master-slave structure. A PC (master) controls the peripheral devices connected to its USB socket, such as keyboard, mouse, etc. (slave). Nowadays, thanks to so-called distributors, it is possible to connect several peripheral devices via a USB socket. The maximum number per socket (port) is 127 peripheral devices. The maximum distance between two USB hubs and connections must not exceed 5 meters to ensure proper function. Please note that the more nested the hub levels, the slower the transfer works.
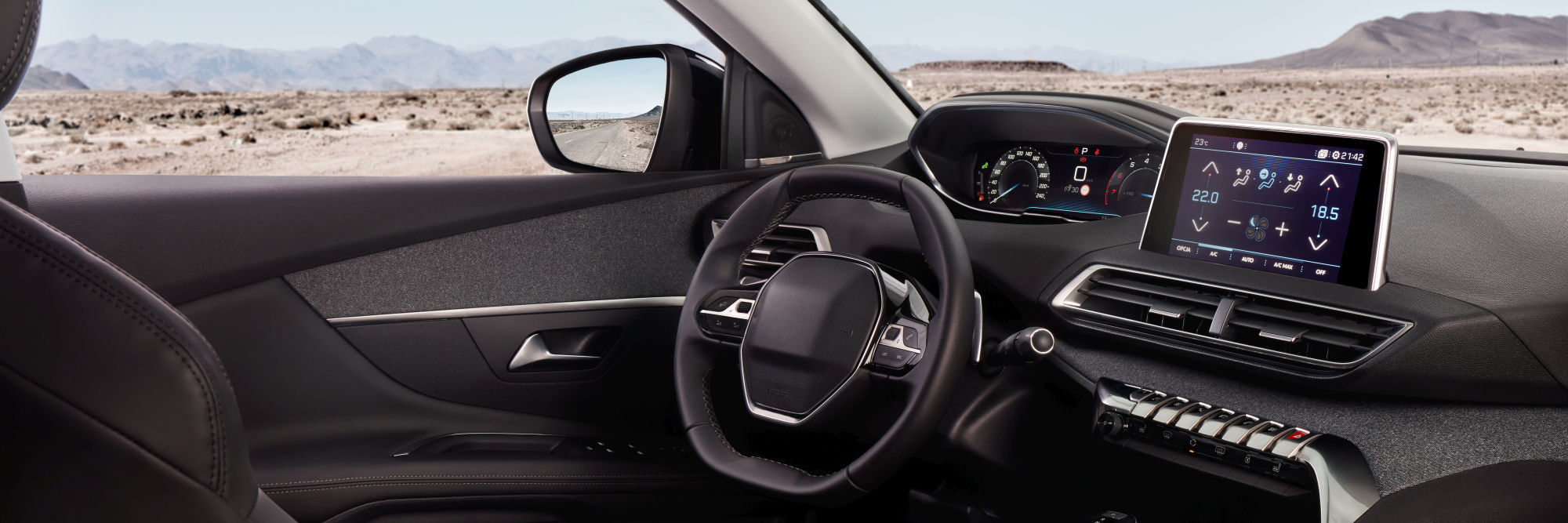
USB specifications in automobiles
USB has existed for decades and is constantly being developed. There are various specifications that determine the current and voltage strength as well as the transmission speed. In older models of a car, USB 2.0 is used, the transmission speed of which is sufficient to transfer MP3 data to the on-board computer for music playback. However, the charging voltage of 0.5 V is too low to charge modern devices (smartphones, tablets) that require a charging voltage of at least 2.4 V. Today, the USB connection is often used to display apps and content from smartphones on the large displays of the vehicles (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto, MirrorLink). Since the speed of USB 2.0 reaches its limits here, USB 3.0 is used in such applications, which enables a transmission speed of more than 20 times that of USB 2.0. Another innovation, the USB Type C connection, which is part of the standard equipment of today's premium smartphones, has recently been used by some car manufacturers. The advantage of USB Type C in automobiles is the simultaneous availability of USB Power Delivery, which enables a significantly higher charging capacity. A maximum charging power of 2.5 W can be called up where USB 2.0 is still used. With USB Power Delivery, on the other hand, this is around 100 W. This enables a whole range of USB peripheral devices such as monitors, seat heaters and other power-hungry devices to be connected.
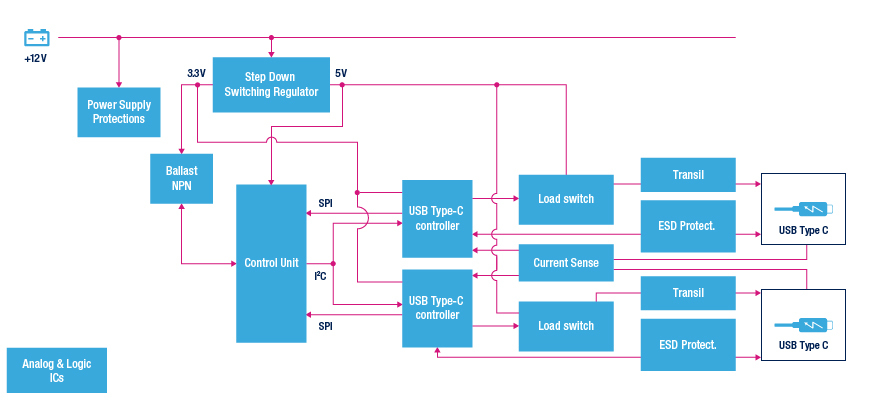
Which manufacturers offer suitable USB systems?
Microchip is one of the first manufacturers to offer a wide range of USB systems for the automotive sector. They range from USB 2.0 applications to USB 3.1 (Superspeed USB).
The most advanced system, USB7002, offers integrated power supply circuits and a 32-bit microcontroller for fast charging. With the USB systems UPD301A, UPD350, USB4916 and USB7050, Microchip also offers solutions for charging with USB Power Delivery in automobiles.
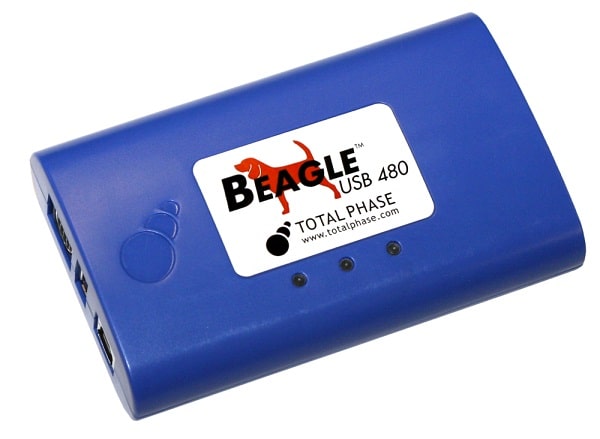
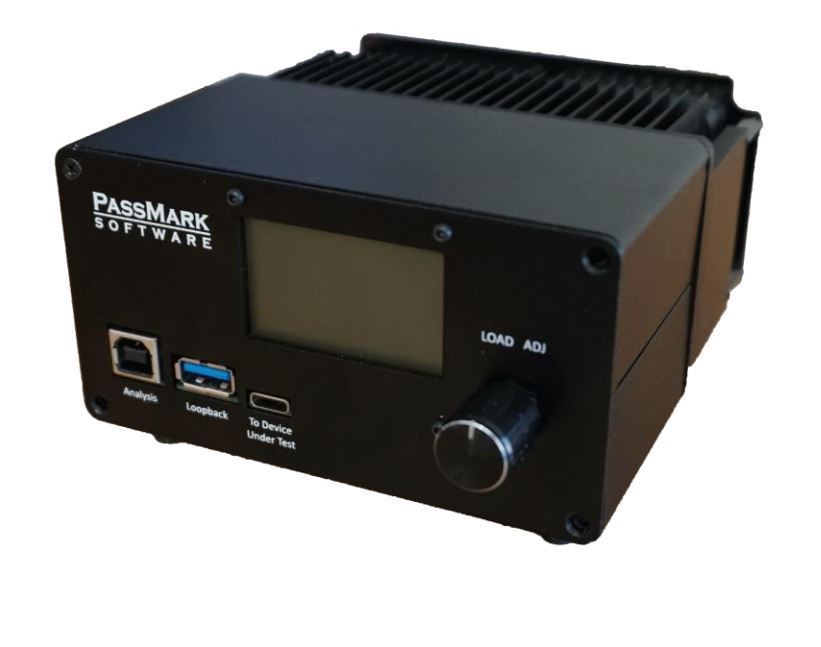
Development and testing of USB designs in the automotive sector
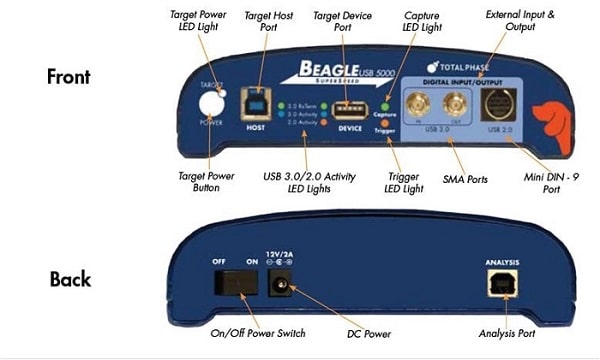
Manufacturers of peripheral devices must ensure compatibility with the automotive USB controller. This poses a major challenge for test and development engineers due to the variety of USB controllers and USB specifications. A protocol analyzer is a suitable measuring device for such requirements